
Breaking into a data science role at a leading company like Walmart requires not only a strong grasp of technical skills but also a deep understanding of probability and statistics. Probability plays a crucial role in decision-making, forecasting, and modeling — all core to the work data scientists do at Walmart, especially in areas such as supply chain optimization, customer behavior analysis, and pricing strategies.
In this article, we’ll walk you through 3 commonly asked probability questions in Walmart data scientist interviews, complete with detailed explanations and solutions to help you prepare with confidence.
Question 1: The Biased Coin Toss
Problem:
You have a biased coin that lands heads with a probability of 0.6 and tails with a probability of 0.4. You toss the coin three times. What is the probability that you get exactly two heads?
Solution:
This is a classic binomial probability problem.
Given:
- Number of trials (n) = 3
- Probability of success (head) p = 0.6
- Probability of failure (tail) q = 0.4
- We want exactly k = 2 heads.
Binomial Formula:

Final Answer: 0.432
Question 2: Conditional Probability — Item Recommendation
Problem:
70% of customers who visit Walmart’s website buy at least one item. Among those who buy, 60% also leave a review. Among those who don’t buy, only 10% leave a review.
What is the probability that a customer who left a review actually bought an item?
Solution:
We are given conditional probabilities and need to find the inverse conditional probability — i.e., using Bayes’ Theorem.
Let:
- B = customer bought an item
- R = customer left a review
We want:

Given:
- P(B)=0.7
- P(R∣B)=0.6
- P(R∣B′)=0.1
- P(B′)=0.3
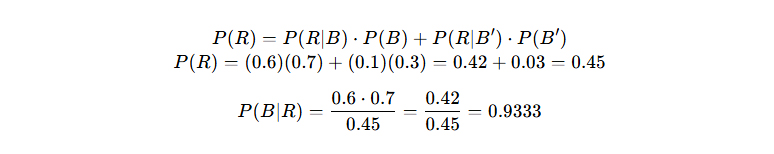
Final Answer: ~93.33%
Question 3: Expected Value — Inventory Demand
Problem:
A store manager at Walmart estimates that the daily demand for a product follows this probability distribution:
| Units Demanded | Probability |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.1 |
| 1 | 0.2 |
| 2 | 0.4 |
| 3 | 0.2 |
| 4 | 0.1 |
What is the expected number of units demanded per day?
Solution:
The expected value (mean) of a discrete random variable is:

Final Answer: 2 units per day
- Binomial problems assess understanding of discrete distributions, which is key for modeling user behaviors or purchase frequencies.
- Bayes’ Theorem is foundational for recommendation systems, fraud detection, and inference under uncertainty.
- Expected value is critical in inventory planning, forecasting, and cost modeling — all important to Walmart’s operations.
Pro Tips for Walmart Data Science Interviews
- Master the fundamentals: Focus on distributions, expectation, variance, conditional probability, and independence.
- Practice real-life scenarios: Walmart loves practical applications. Relate your answers to business problems.
- Explain your reasoning: They’re looking for clear thinkers. Walk through your assumptions and logic.
Final Thoughts
Cracking a data science interview at Walmart means demonstrating a deep, intuitive understanding of probability. These three questions give you a solid foundation to prepare and shine. Want to take your prep further? Practice variations, dive into Walmart’s business model, and explore case studies related to retail data.
Good luck — you’ve got this!
ثلاثة أسئلة شائعة في مقابلات علماء البيانات في وول مارت (مع حلول مفصلة)

يتطلب العمل في مجال علم البيانات
Why These Questions Matter
Walmart في شركة رائدة مثل
ليس فقط فهماً عميقاً للمهارات التقنية بل أيضاً فهماً عميقاً للاحتمالات والإحصاءات، إذ تلعب الاحتمالات دوراً حاسماً في صنع القرار والتنبؤ والنمذجة
Walmart وهي جميعها عناصر أساسية في عمل علماء البيانات في
لا سيما في مجالات مثل تحسين سلسلة التوريد وتحليل سلوك العملاء واستراتيجيات التسعير
في هذه المقالة سنشرح لك ثلاثة أسئلة شائعة
Walmart في مقابلات علماء البيانات في
مع شرح وحلول مفصلة لمساعدتك على الاستعداد بثقة
السؤال الأول: رمي العملة المعدنية المتحيز
:المشكلة
لديك عملة معدنية متحيزة واحتمال ظهور وجهها (الصورة) هو 0.6 ووجهها (الكتابة) هو 0.4 رميت العملة ثلاث مرات، فما هو احتمال ظهور وجهين فقط (الصورة)؟
:الحل
هذه مسألة احتمالية ثنائية تقليدية
المعطيات
3 = (n) عدد المحاولات
0.6 = (p) احتمال النجاح (الصورة)
0.4 = (q) احتمال الفشل (الكتابة)
صورتين = (k) نريد بالضبط
: صيغة ثنائية الحدين

الإجابة النهائية: ٠٫٤٣٢
السؤال الثاني: الاحتمال الشرطي – توصية المنتج
:المشكلة
٧٠٪ من زوار موقع وول مارت الإلكتروني يشترون منتجاً واحداً على الأقل
من بين المشترين ٦٠٪ يتركون تقييماً أيضاً
ومن بين الذين لا يشترون ١٠٪ فقط يتركون تقييماً
ما هو احتمال أن يكون العميل الذي ترك تقييماً قد اشترى المنتج بالفعل؟
:الحل
لدينا احتمالات شرطية وعلينا إيجاد الاحتمال الشرطي العكسي
:لنفترض أن
B = عميل اشترى منتجاً
R = عميل ترك تقييماً
:نريد
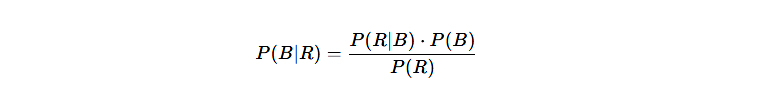
:المعطيات
- P(B)=0.7
- P(R∣B)=0.6
- P(R∣B′)=0.1
- P(B′)=0.3

%الإجابة النهائية: ~93.33
السؤال الثالث: القيمة المتوقعة – طلب المخزون
:المشكلة
يقدر مدير متجر في وول مارت أن الطلب اليومي على منتج ما يتبع توزيع الاحتمالات التالي
| الاحتمال | الوحدات المطلوبة |
|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0 |
| 0.2 | 1 |
| 0.4 | 2 |
| 0.2 | 3 |
| 0.1 | 4 |
ما هو عدد الوحدات المطلوبة يومياً؟
: الحل
: القيمة المتوقعة (المتوسط) لمتغير عشوائي منفصل هي

الإجابة النهائية: وحدتان يومياً
لماذا هذه الأسئلة مهمة؟
تُقيّم المسائل ثنائية الحدّ فهم التوزيعات المنفصلة وهو أمرٌ أساسيٌّ لنمذجة سلوكيات المستخدمين أو تكرارات الشراء *
تُعدّ نظرية بايز أساساً لأنظمة التوصية وكشف الاحتيال والاستدلال في ظلّ عدم اليقين *
تُعدّ القيمة المتوقعة بالغة الأهمية في تخطيط المخزون والتنبؤ ونمذجة التكلفة وكلها عوامل بالغة الأهمية لعمليات وول مارت *
:نصائح احترافية لمقابلات وول مارت في علم البيانات
أتقن الأساسيات: ركّز على التوزيعات والتوقعات والتباين والاحتمال الشرطي والاستقلالية
تدرّب على سيناريوهات واقعية: تُحبّ وول مارت التطبيقات العملية، لذا اربط إجاباتك بمشاكل العمل
اشرح منطقك: إنهم يبحثون عن مفكرين ذوي رؤى بعيدة، لذا استعرض افتراضاتك ومنطقك
:الخاتمة
يعني اجتياز مقابلة علم بيانات في وول مارت إظهار فهم عميق وبديهي للاحتمالات، إذ تمنحك هذه الأسئلة الثلاثة أساساً متيناً للاستعداد والتألق، فهل ترغب في تطوير استعدادك؟ مارس التنوعات واستكشف نموذج أعمال وول مارت واستكشف دراسات الحالة المتعلقة ببيانات البيع بالتجزئة

