
In today’s data-driven world, the role of a data analyst has emerged as one of the most sought-after professions. A “real” data analyst is not merely someone who understands numbers but a professional capable of extracting meaningful insights from data and translating them into actionable strategies. Becoming a proficient data analyst requires a combination of technical expertise, business acumen, and a continuous learning mindset. This essay explores the essential steps to becoming a successful data analyst.
1. Acquiring Foundational Knowledge
The journey to becoming a data analyst begins with understanding the basics. Foundational knowledge in mathematics and statistics is crucial since these form the backbone of data analysis. Concepts such as probability, descriptive statistics, and hypothesis testing are indispensable tools for interpreting data. Moreover, familiarity with Excel is often a stepping stone, as it allows beginners to perform data cleaning and basic analysis tasks.
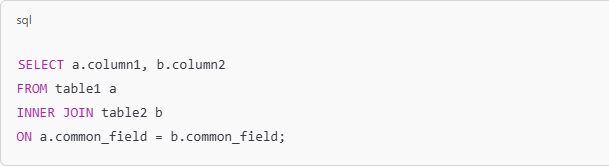
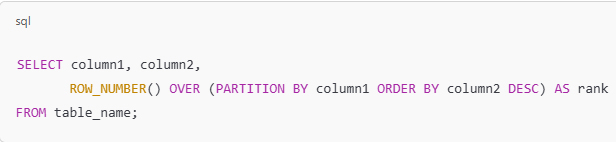
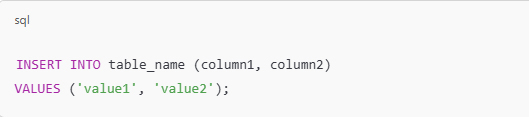
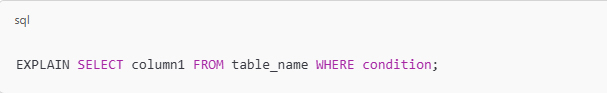
A firm grasp of SQL (Structured Query Language) is also essential. SQL enables analysts to extract and manipulate data from relational databases, which is a fundamental aspect of the job. These skills form the core of data analysis and serve as the foundation for more advanced techniques.
2. Mastering Technical Skills
A “real” data analyst is equipped with advanced technical skills that go beyond basic tools. Learning programming languages such as Python and R is highly recommended. These languages allow analysts to perform complex data manipulation, automate repetitive tasks, and create visualizations. Libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib in Python, or ggplot2 in R, are invaluable for data analysis.
In addition to programming, proficiency in data visualization tools like Tableau and Power BI is essential. These tools enable analysts to present data in an intuitive and visually appealing way, making it easier for stakeholders to grasp insights. As data grows in size and complexity, familiarity with big data technologies like Hadoop or Spark can also provide a competitive edge.
3. Understanding the Business Context
Technical skills alone do not make a great data analyst. The ability to understand the business context is equally important. A real data analyst knows how to ask the right questions and align their analysis with business objectives. This involves identifying key performance indicators (KPIs), understanding the target audience, and framing insights in a way that drives decision-making.
Business acumen also includes effective communication. Analysts must bridge the gap between raw data and business strategies by presenting findings in a clear and concise manner. Storytelling with data is a powerful skill that ensures stakeholders can act on the insights provided.
4. Gaining Practical Experience
Real-world experience is crucial for becoming a proficient data analyst. Internships and entry-level positions provide exposure to practical challenges, from handling messy datasets to meeting tight deadlines. Working on personal projects is another excellent way to build experience. By analyzing publicly available datasets, aspiring analysts can create a portfolio that showcases their skills and problem-solving abilities.
Online platforms like Kaggle offer opportunities to work on real-world problems and participate in competitions, allowing analysts to benchmark their skills against a global community. These experiences not only enhance technical proficiency but also foster a deeper understanding of how to approach complex problems.
5. Adopting a Growth Mindset
The field of data analytics is dynamic, with new tools, techniques, and technologies emerging regularly. To stay relevant, a data analyst must adopt a growth mindset and commit to continuous learning. Online courses, certifications, and webinars are excellent resources for staying updated. Certifications from organizations like Google, IBM, or Microsoft can validate an analyst’s skills and make them more attractive to employers.
Networking within the data analytics community can also provide valuable insights into industry trends and best practices. Attending conferences, joining professional groups, and engaging in online forums can help analysts stay connected and informed.
6. Building Soft Skills
While technical and analytical skills are critical, soft skills often differentiate a good data analyst from a great one. Problem-solving is at the heart of data analysis, requiring creativity and critical thinking. Time management is equally important, as analysts often juggle multiple projects with competing deadlines.
Teamwork and collaboration are vital, as analysts frequently work with cross-functional teams, including marketing, finance, and operations. The ability to communicate effectively, both verbally and visually, ensures that insights are understood and acted upon.
Conclusion
Becoming a “real” data analyst is a multifaceted journey that combines technical expertise, business understanding, and practical experience. It requires a solid foundation in statistics and programming, mastery of visualization tools, and the ability to communicate insights effectively. By continuously learning and adapting to new challenges, aspiring analysts can establish themselves as valuable contributors in the ever-evolving world of data analytics. With dedication and persistence, anyone can transform raw data into powerful insights that drive meaningful change.
الخطوات الأساسية لتصبح محلل بيانات ناجحاً

في عالم اليوم الذي تحركه البيانات برز دور محلل البيانات كواحد من أكثر المهن المطلوبة، فمحلل البيانات “الحقيقي” ليس مجرد شخص يفهم الأرقام ولكنه محترف قادر على استخراج رؤى ذات مغزى من البيانات وترجمتها إلى استراتيجيات قابلة للتنفيذ، إذ يتطلب أن تصبح محلل بيانات ماهراً مزيجاً من الخبرة الفنية وفطنة الأعمال وعقلية التعلم المستمر
يستكشف هذا المقال الخطوات الأساسية لتصبح محلل بيانات ناجحاً
1. اكتساب المعرفة الأساسية
تبدأ الرحلة لتصبح محلل بيانات بفهم الأساسيات، فالمعرفة الأساسية في الرياضيات والإحصاء أمر بالغ الأهمية لأنها تشكل العمود الفقري لتحليل البيانات، والمفاهيم مثل الاحتمالات والإحصاء الوصفي واختبار الفرضيات هي أدوات لا غنى عنها لتفسير البيانات، علاوة على ذلك غالباً ما تكون الألفة مع برنامج إكسل بمثابة حجر الأساس بحيث تسمح للمبتدئين بأداء مهام تنظيف البيانات والتحليل الأساسية
(لغة الاستعلام الهيكلية) SQL يعد الفهم القوي لـ
أمراً ضرورياً أيضاً، إذ تمكّن هذه اللغة المحللين من استخراج البيانات ومعالجتها من قواعد البيانات العلائقية وهو جانب أساسي من الوظيفة، بحيث تشكل هذه المهارات جوهر تحليل البيانات وتعمل كأساس لتقنيات أكثر تقدماً
2. إتقان المهارات الفنية
يتمتع محلل البيانات “الحقيقي” بمهارات فنية متقدمة تتجاوز الأدوات الأساسية، إذ يوصى بشدة بتعلم لغات البرمجة
إذ أن هذه اللغات R مثل بايثون و
تسمح للمحللين بإجراء معالجة معقدة للبيانات وأتمتة المهام المتكررة وإنشاء تصورات، لذا تعد المكتبات
في بايثون Pandas و NumPy و Matplotlib مثل
لا تقدر بثمن لتحليل البيانات R في ggplot2 أو
بالإضافة إلى البرمجة فإن إتقان أدوات تصور البيانات
أمر ضروري Tableau و Power BI مثل
بحيث تمكن هذه الأدوات المحللين من تقديم البيانات بطريقة بديهية وجذابة بصرياً مما يسهل على أصحاب المصلحة فهم الرؤى، وعليه ومع نمو حجم البيانات وتعقيدها يمكن أن توفر الألفة بتقنيات البيانات الضخمة
أيضاً ميزة تنافسية Hadoop أو Spark مثل
3. فهم سياق العمل
لا تكفي المهارات الفنية وحدها لصنع محلل بيانات رائع، إذ أن القدرة على فهم سياق العمل مهمة بنفس القدر، فيعرف محلل البيانات الحقيقي كيفية طرح الأسئلة الصحيحة ومواءمة تحليله مع أهداف العمل، فيتضمن هذا تحديد مؤشرات الأداء الرئيسية وفهم الجمهور المستهدف وصياغة الأفكار بطريقة تدفع عملية اتخاذ القرار
تتضمن الفطنة التجارية أيضاً التواصل الفعال بحيث يجب على المحللين سد الفجوة بين البيانات الخام واستراتيجيات العمل من خلال تقديم النتائج بطريقة واضحة وموجزة، وعليه فإن سرد القصص باستخدام البيانات مهارة قوية تضمن قدرة أصحاب المصلحة على التصرف بناءً على الأفكار المقدمة
4. اكتساب الخبرة العملية
إن الخبرة في العالم الحقيقي أمر بالغ الأهمية لكي تصبح محلل بيانات ماهراً، فتوفر التدريبات والمناصب الأولية التعرض للتحديات العملية من التعامل مع مجموعات البيانات الفوضوية إلى تلبية المواعيد النهائية الضيقة، فيعد العمل في المشاريع الشخصية طريقة ممتازة أخرى لبناء الخبرة، فمن خلال تحليل مجموعات البيانات المتاحة للجمهور يمكن للمحللين الطموحين إنشاء محفظة تعرض مهاراتهم وقدراتهم على حل المشكلات
Kaggle توفر المنصات عبر الإنترنت مثل
فرصاً للعمل على مشاكل العالم الحقيقي والمشاركة في المسابقات مما يسمح للمحللين بمقارنة مهاراتهم بمجتمع عالمي، فلا تعمل هذه التجارب على تعزيز الكفاءة الفنية فحسب بل تعزز أيضاً فهماً أعمق لكيفية التعامل مع المشكلات المعقدة
5. تبني عقلية النمو
يعتبر مجال تحليل البيانات ديناميكياً مع ظهور أدوات وتقنيات جديدة بانتظام للبقاء على صلة يجب على محلل البيانات تبني عقلية النمو والالتزام بالتعلم المستمر، فالدورات التدريبية عبر الإنترنت والشهادات والندوات عبر الإنترنت هي موارد ممتازة للبقاء على اطلاع
Google أو IBM أو Microsoft ويمكن للشهادات من منظمات مثل
التحقق من صحة مهارات المحلل وجعلها أكثر جاذبية لأصحاب العمل
يمكن أن توفر الشبكات داخل مجتمع تحليل البيانات أيضاً رؤى قيمة حول اتجاهات الصناعة وأفضل الممارسات، إذ يمكن أن يساعد حضور المؤتمرات والانضمام إلى المجموعات المهنية والمشاركة في المنتديات عبر الإنترنت المحللين على البقاء على اتصال وإطلاع
6. بناء المهارات الشخصية
في حين أن المهارات الفنية والتحليلية بالغة الأهمية فإن المهارات الشخصية غالباً ما تميز محلل البيانات الجيد عن المحلل المتمرس بحيث يعتبر حل المشكلات هو جوهر تحليل البيانات ويتطلب الإبداع والتفكير النقدي، كما أن إدارة الوقت مهمة بنفس القدر حيث غالباً ما يتنقل المحللون بين مشاريع متعددة ومواعيد نهائية متنافسة
إن العمل الجماعي والتعاون أمران حيويان حيث يعمل المحللون غالباً مع فرق متعددة الوظائف بما في ذلك التسويق والتمويل والعمليات، وتضمن القدرة على التواصل بشكل فعال سواء لفظياً أو بصرياً فهم الأفكار والعمل عليها
الخلاصة
إن التحول إلى محلل بيانات “حقيقي” هو رحلة متعددة الأوجه تجمع بين الخبرة الفنية وفهم الأعمال والخبرة العملية ويتطلب الأمر أساساً متيناً في الإحصاء والبرمجة وإتقان أدوات التصور والقدرة على توصيل الأفكار بشكل فعال، ومن خلال التعلم المستمر والتكيف مع التحديات الجديدة يمكن للمحللين الطموحين ترسيخ أنفسهم كمساهمين قيمين في عالم تحليل البيانات المتطور باستمرار، وبالتفاني والمثابرة يمكن لأي شخص تحويل البيانات الخام إلى رؤى قوية تدفع إلى تغيير ذي مغزى























You must be logged in to post a comment.